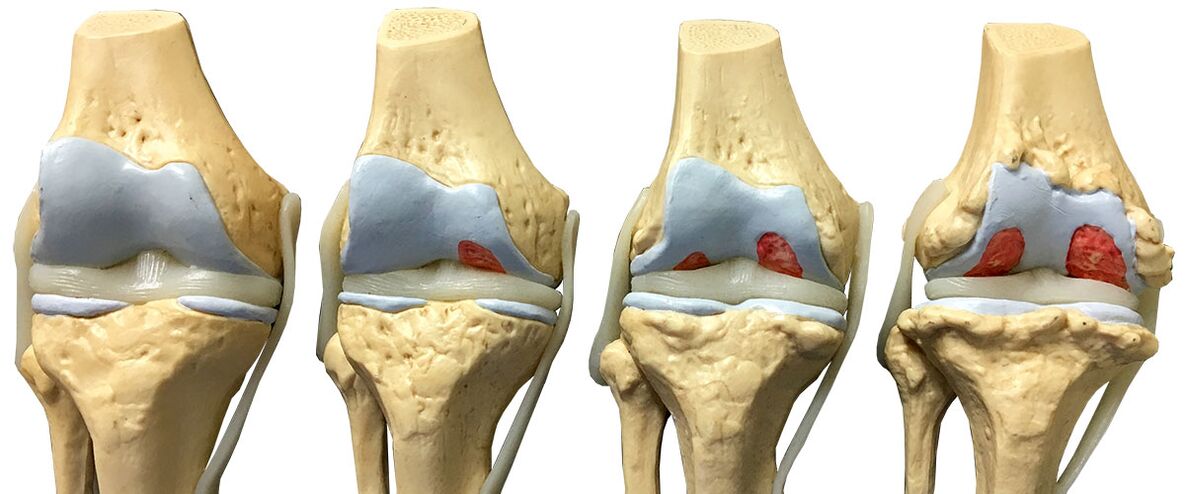
The deforming arthrosis of the knee joint is called gonarthrosis in the drug-it is a degenerative-dystrophic disease in the cartilage of hyaline of the knee, which covers the warts of the femur and tibia.
With arthrosis of the knee joint, the symptoms develop gradually, for years the main manifestation of the disease is pain, stiffness during movement. Gonarthrosis is considered to be the most common disease among arthrosis of other joints, such as hip arthrosis, arthrosis of the elbows or shoulder joints and phalanges of the fingers.
Most often the disease affects individuals over 40, women are most susceptible to arthrosis. Sometimes it develops in young people against the background of injuries or in athletes of excessive loads.
Symptoms of knee arthrosis.
There may be several symptoms of a serious illness (bone arthritis, joints) and not all appear at once, but gradually cartilage tissues are destroyed. Consider the symptoms of knee arthrosis at all stages (stages) of the disease. At the initial stage, the patient has a minimum of discomfort, but even mild but quite acute knee pain begins to appear. The problem of becoming travel or long tourism becomes problematic. In addition, the pain that has suffered the body begins to worsen and the person is already uncomfortable in the knees, after some physical exertion or when lifted from sedentary positions when there is a load in the lower limbs. In such cases, they experience acute pain in the cartilage or in the joint itself. Such pain goes away quickly, but it returns every time. In the next stage of the disease, not only the painful sensations intensify, but also begin to change their knee. Due to the fluid accumulated in cartilage tissue, the knees can become spherical and slightly swell. Besides, everything is worse. If the disease is left untreated, the blood circulation process is disturbed in the knee, the hyaline cartilage area dries and the cartilage itself may crack, after which it will begin to collapse and different types of growth will begin to appear on the bone structure. At this stage, the movement of cartilage is already very difficult and every step is given to a person with difficulty. Walking causes severe pain that practically does not end, and discomfort, cartilage degeneration occurs. The last stage of the disease is when the knee joint is already completely affected, there is no cartilage tissue in the knee and a person without support simply cannot sit and stand up, he cannot completely move without experiencing severe pain in such movements. The causes of knee arthrosis. Knee arthrosis can hit a person for a number of reasons - this is age (over the years when cartilage wears out) and intense physical therapy of the leg or legs and various types of knee injuries and many others. The main causes of the development of arthrosis: To avoid damage, you should consult a rheumatologist for qualified help on time. What happens to the joint with arthrosis. At each stage of the disease, its modifications appear in cartilage, in the joints and bones of the knees. So, at the very beginning of the development of the disease, cartilage softens strongly, becomes very vulnerable. In addition, the micro -cracks and small tears, which gradually increase, appear on the surface of the joints. The next stage - the cartilage begins to grow and increase the thickness. The last stage is the complete destruction of cartilage on a particular or some specific section of the joint. Knee arthrosis, degree of disease All rheumatologists reveal the three degrees of arthrosis of the human knee. First. It is characterized by a slight narrowing of the slots directly between the joints themselves, which leads to mild discomfort and without restriction of movement. The second. On it, doctors note a pronounced narrowing of cracks between the joints, the formation of osteophytes and cysts, the appearance of a strong crunch in the knees. The third and the last. There is a change in the forms of osteophytes, there is a partial or complete change (destruction) of the bones, the movement of the legs in the knees becomes impossible. Common symptoms include: The main symptoms of knee arthrosis joint The main (main, according to Russia doctors), the symptoms of arthrosis are four. These include: After carefully examining the patient, the rheumatologist evaluates the situation, turning his gaze to changes visible from the eye in the areas of one knee or both and their direct mobility. The drilling method sets the sites of pain and crunch, as well as the intensity of these pains. In addition to X -ray for the patient, the doctor prescribes computed tomography and (or) MRI. These studies are necessary to establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe proper treatment. The treatment of arthrosis at each stage of the knee joint includes: What gives effective therapy. Effective therapy prescribed by a doctor contributes to: When eliminating knee arthrosis, exercise therapy plays a special role, a special diet based on legumes and dairy products and massage. If the prescribed therapy for one reason or another does not show the desired result, the patient is prescribed surgery to install a special prosthesis replacing the joint. The competent treatment with arthrosis of the cartilage tissues of the knee joint (disorders of the cartilage composition), prescribed by the rheumatologist, includes a whole complex of medicines. This treatment complex usually includes: Most often, for the treatment of knee cartilage arthrosis, doctors prescribe ibuprofen to any producer, indomethacin also for production, ketoprofen, diclofenac, pyroxics and others. The appointment of these drugs contributes to the rapid elimination of pain, as a result of which the patient can start beneficial treatment in other ways - the massage method, medical exercises, etc. As for the ointments, most often for the patient, the use (rubbing with massage movements in the area of inflamed) of such drugs in the form of dense fat (creams) and gels such as diclofenac, festum, Ferbedon, transivazine, dolgite and others. The list of special gels and ointments - external preparations for the joints of the modern pharmacological market is very wide and varied and therefore, at the recommendation of a doctor, the patient can choose from the total number of the most appropriate and effective specifically in his case. After using these compresses, about 75% of patients report a significant improvement in their condition, reduce pain and almost complete disappearance of characteristic knee bark. ShouldRemember that recipes for traditional medicine do not cure the disease, they can supplement the therapeutic course of medication treatment, which makes this course more effective. If you prepare any of the means for traditional medicine or properly prepare raw materials for such an instrument, you are not able to buy such components at a pharmacy or to ask to collect plants from knowledgeable people (folk healers, grandmothers). A special place for the treatment of arthrosis in the knees is occupied by special therapeutic gymnastics (exercises). Patients are prescribed, regardless of the treatment process, to improve the flow and leakage of blood into the affected area, increase muscle strength and prevent contractures. Shown together with the use of special medicines. LFK for arthrosis is by no means a specific treatment, it is an auxiliary method for combating the disease, which is prescribed in combination with a course of special medicines. Several exercises from therapeutic gymnastics for treatment and prevention: Exercise therapy for the treatment of arthrosis of the joint cartilage of the knee will bring more benefits if you combine therapeutic exercises with special massage. Visible changes in the condition using physiotherapy exercises in the patient may occur in 7-10 days. If you are not able to do exercises yourself, it is better to refuse exercises. Summarizing, they would like to notice that after finding the first symptoms of the disease and these are pain in the knee joints and a characteristic crunch, they immediately go to the doctor and begin special treatment with medication. A diet that will help with arthrosis. Immediately, if you find arthrosis or to prevent the disease, review the diet of your usual diet. There should be a stewed dish or cooked daily diet. It is best if foods that have a beneficial effect on bones, ligaments, joints and cartilage are used in food. Such products include: all legumes, cottage cheese, solid cheese varieties, soup, roasted fish, hazelnuts, almonds, pumpkin, zucchini, carrots, broccoli and cauliflower prepared based on bones. A diet that is described above is not a specific method of treatment, for effective treatment should be used in combination with medicines, medical exercises and massage. Knee arthrosis is a disease in which it is hereditary predisposition to it. So, if you are a woman and your mother suffers from osteoarthritis in any form (not with all colleagues), then the likelihood of this disease is 2-3 times higher than on average in the population. If you have sisters and they are also ill with arthrosis, then the likelihood of its occurrence is even more. In addition, there are diseases with hereditary predisposition, with connective tissue affected - So -Called Collagenos, which include, for example, Sticler syndrome. In the presence of such defects from collagen, a substance that is part of the relationships - the likelihood of developing the disease also increases. In part of this group of causes of knee arthrosis, endocrine diseases are adjacent: diabetes mellitus, lack of female sex hormones in menopause and a number of other conditions. Unfortunately, the more jewelry the person becomes, the greater the risk of osteoarthrosis. This is due to the fact that with age the ability of cartilage to regeneration and restoration falls and metabolism in the joints worsens. So, if at the age of 45 this disease suffers from 1, 5 to 3-4% of the population (US data), then almost every third person is ill in the interval from 45 to 65 years (30%). And at the age of 65 to 85 years, the frequency of development of the disease jumps to 80 percent or more! In addition, in adulthood patients, the development of the disease is influenced not only by age in itself, but also by hormonal changes. So in menopause women, the likelihood of developing osteoarthritis is sharply increased. This is due to the fact that estrogens - female sex hormones - regulate the processes of metabolism in the joints, cartilage, bones and ligaments. When they become smaller (when menopause), the metabolism in these tissues worsens and the risk of osteoarthrosis increases sharply. Inflammation of the knee joint (arthritis, more precisely, drives) is one of the most common causes of gonarthrosis. Unfortunately, most of the microorganisms that penetrate the joint and cause its inflammation contribute to the fact that delicate cartilage is deformed. At the same time, its nutrition deteriorates significantly, the shape of the cartilage surfaces of the bones changes, etc. For all these reasons, the normal drainage of cartilage in the joint bones is impaired. This leads to additional cartilage trauma, worsens the volume of movement in the joint and to the end creates very fertile soil for the development of osteoarthrosis. Another common cause of the disease is the presence of knee injuries and surgery on it. Very often there is one and the other at the same time - for example, when, as a result of sports injuries, surgical removal of the meniscus is performed. The normal function of the joint is impaired, the loading of the cartilage changes, intensifying in atypical places and as a result, the osteoarthrosis of the knee is formed. Cartilage tissue in the joints is one of the few whose nutrition does not happen by delivering nutrients through the blood vessels. Cartilage is "eaten" by diffusion of nutrients from synovial fluid, as well as directly from the pineal glands according to the same principle. This is a rather subtle and fragile mechanism, therefore, if various metabolic disorders occur in the body, it can break and stop working. Therefore, some diseases in which metabolism in the body is severely impaired can contribute to osteoarthrosis. Such diseases include primary and secondary gout, joint chondromatosis, hemochromatosis, octrosis, as well as Wilson-Konovov's disease and a number of other diseases. In addition, endocrine diseases can be added to this group, which also affects the metabolism throughout the body - diabetes mellitus and lack of female sex hormones (estrogen) in the elderly due to menopause. As mentioned earlier, cartilage nutrition is a very fine mechanism that can disrupt not only problems with metabolism, but also increased loads of the knee joint. This happens quite often with intense sports, as well as when a person's work involves high physical activity, as well as prolonged standing on his feet, without the ability to sit and relax. At the same time, some muscle groups (such as the muscles of the lower legs and thighs) are overworn. This impairs nutrition in the muscles and joints, which means that there are problems with the metabolism inside the cartilage, when cartilage simply do not have time to recover after such intense exercise in the joint. Knee arthrosis should be differentiated (distinguished) by rheumatic, inflammatory and some other diseases with similar symptoms. For this, a standard test standard has been adopted, which includes a general biochemical blood test, radiographic examination, MRI and ultrasound. With arthrosis, a blood test does not reveal significant abnormalities from the norm. The change in blood composition, an increase in the level of immune cells and antibodies usually shows another disease. Since arthrosis does not manifest in analysis in any way, the only reliable way to diagnose it is a hardware examination. X -ray, as the most common and cheapest method of examination, is able to identify relatively accurately arthrosis and its stage. In the photo, structural changes in the joints and bones differ clearly. X -ray study enables the detection of structural deformities, determining defects in the joint surfaces. For reliable gonarthrosis and the stage of its development, additional examination is used in connection with X -Ray: ultrasound, MRI or CT apparatus. The methodology for the diagnosis of arthrosis is designed to guarantee the accurate detection of the disease in the most stages of development, which will effectively treat it. Unfortunately, due to the specificity of the disease, the effectiveness of this approach is small: patients tend not to pay attention to poor pain and mild chromium and are led to the doctor already in the second or third stage of gonarthrosis. Preventive measures are aimed at eliminating the risk factors that lead to the development of arthrosis. It is recommended that you participate in moderate physical activity. In this case, possible injury, surge and hypothermia of the joints should be avoided. As noted above, no link was established between the diet and the risk of developing arthrosis. However, it is recommended to reduce the consumption of salted and spicy foods, alcohol and cigarettes: this will improve the general condition of the body and reduce the load on the joint. In the presence of a family history, which shows a genetic predisposition, a physical examination should be regularly examined. In general, prevention of arthrosis is to lead a moderate lifestyle. It is important not to start the disease and consult a doctor with the slightest suspicion of arthrosis.